Master Guide: what is capacity planning and how it works
Discover what is capacity planning and how it balances resources with demand. Get practical steps, strategies, and tools to boost efficiency.

At its core, capacity planning is all about striking a perfect balance. It’s the process of making sure your business resources—your people, your equipment, your technology—are perfectly aligned with the demands of your customers.
The goal? Have exactly what you need, right when you need it. This way, you sidestep both the financial drain of having too much and the frustrating customer experience of having too little.
What Is Capacity Planning

Think about running a busy coffee shop. Your "capacity" is everything from your baristas and espresso machines to your inventory of coffee beans and milk. If you schedule too many people on a quiet afternoon, you're paying for idle hands. But if you're understaffed during the morning rush, you'll have a line out the door and customers walking away.
Capacity planning is the discipline of getting that balance just right. It's a forward-looking strategy that helps you predict what's coming and make sure your resources are ready. The whole point is to run at peak efficiency, cutting out waste while keeping customers happy.
Why It Matters More Than You Think
When businesses fly blind without a capacity plan, they're always in reactive mode—scrambling to catch up with demand instead of preparing for it. This almost always leads to the same old problems: last-minute hiring frenzies, blown project deadlines, and budgets that spiral out of control.
Good capacity planning flips the script, turning that chaos into a structured, data-informed strategy.
It empowers you to get ahead of the big questions every business faces:
- Do we have enough people on deck for the holiday sales rush?
- Can our current servers handle a sudden doubling of our user base?
- Should we greenlight that new production line now, or can it wait six months?
Answering these questions ahead of time leads to smarter, more confident decisions that pave the way for sustainable growth. For anyone looking to apply these principles specifically to their team, a great resource is this guide on mastering workforce capacity planning.
At its heart, capacity planning is about replacing guesswork with a calculated strategy. It provides a roadmap that connects your long-term goals with the day-to-day resources required to achieve them.
Ultimately, this isn’t just some operational tick-box exercise. It's a fundamental business discipline that directly impacts your bottom line, your customer loyalty, and your ability to grow without breaking things. When you get it right, you make sure your resources are always an asset, never a liability.
The Three Horizons of Capacity Planning
Truly effective capacity planning isn’t a one-and-done activity. It’s a continuous effort that happens across different timelines, much like using different camera lenses for different shots. You wouldn’t use a wide-angle lens for a close-up portrait, and you wouldn't use a macro lens to capture a sprawling landscape.
In business, we need to plan for the long-term, the medium-term, and the immediate future, each with its own approach.
These three horizons—strategic, tactical, and operational—are designed to work together, connecting the company's big-picture vision with the day-to-day work that makes it happen. Let's break down each one to see how they form a complete, cohesive strategy.
Strategic Planning: The Long-Term View
This is the 30,000-foot view, looking two or more years into the future. Strategic planning is all about the big, foundational decisions that will shape your company's potential for years to come. Think major investments and irreversible commitments.
It’s less about managing what you have and more about building the capacity you’ll need to grow.
For a fast-growing e-commerce business, strategic decisions might look like this:
- Committing to build a new distribution center on the other side of the country to break into a new market.
- Investing millions in a private cloud infrastructure to handle a projected 500% spike in traffic over the next five years.
- Acquiring a smaller logistics company to vertically integrate a critical piece of the supply chain.
These are high-stakes moves. A misstep at the strategic level can hamstring a company for years, making it incredibly expensive and difficult to correct.
Tactical Planning: The Medium-Term Bridge
Tactical planning is the crucial bridge between that long-term vision and daily reality. It typically operates on a six to 24-month timeline. Here, the focus shifts from building new capabilities to optimizing and allocating the resources you either have or will have soon.
If the strategic plan was the decision to build a new warehouse, the tactical plan is all about getting it ready to open its doors.
Tactical planning translates broad strategic goals into a concrete action plan. It's about securing the specific resources—people, equipment, and processes—needed to execute the company's vision over the next one to two years.
Back to our e-commerce example, tactical planning would involve:
- Hiring and Training: Creating a recruitment pipeline and training program to fully staff the new warehouse.
- Technology Rollout: Selecting and implementing the warehouse management system (WMS) and other essential software.
- Supplier Contracts: Vetting and negotiating deals with local and regional shipping partners.
This is where the grand strategy gets its legs. Without solid tactical planning, even the most brilliant strategic investments can fail to deliver on their promise.
Operational Planning: The Daily Grind
Finally, we have operational planning, which is all about the here and now. This is the most immediate horizon, dealing with capacity management on a daily and weekly basis. It's granular, reactive, and all about making the most of what you have today.
This is where the rubber meets the road.
At this level, managers are constantly fine-tuning to balance real-time supply and demand. Examples of operational planning in action include:
- Setting the weekly shift schedule for warehouse pickers and packers based on the latest order forecasts.
- Adjusting safety stock levels for a specific product that's suddenly trending on social media.
- Dynamically reallocating server resources to handle an unexpected traffic surge during a flash sale.
This hyper-detailed, short-term focus is increasingly driven by data. The capacity management analytics market, currently valued around USD 1.98 billion, is expected to grow by nearly 18% each year for the next five years. This boom is fueled by real-time data from IoT and big data analytics, which you can read about in the latest market research on capacity management.
When these three horizons are aligned, a business creates a powerful, seamless flow from its biggest ambitions down to its smallest daily tasks.
To make these differences even clearer, let's look at them side-by-side.
Comparing Strategic, Tactical, and Operational Planning
The table below breaks down the key attributes of each planning horizon, from the timeframe they cover to the types of decisions they influence.
| Attribute | Strategic Planning | Tactical Planning | Operational Planning |
|---|---|---|---|
| Timeframe | 2+ years | 6-24 months | Daily, weekly, monthly |
| Scope | Entire organization, long-term goals | Department or function-level | Specific teams, tasks, and processes |
| Focus | Acquiring major resources, facility location, technology infrastructure | Resource allocation, hiring, subcontracting, process improvement | Scheduling, inventory control, immediate task assignment |
| Decision Impact | High-stakes, long-lasting, difficult to reverse | Medium-term impact, moderately flexible | Immediate impact, highly flexible and reversible |
| Example | "Should we build a new factory in Europe?" | "How will we hire and train 200 staff for the new factory next year?" | "Who is working the assembly line on Tuesday's morning shift?" |
As you can see, each level addresses a distinct set of questions and requires a different mindset. Success depends not on mastering just one, but on orchestrating all three in harmony.
A Practical Four-Step Capacity Planning Framework
Theory is great, but let's get practical. To make capacity planning work, you need a structured, repeatable process. While every business has its quirks, this straightforward, four-step cycle is a reliable way to connect your resources to what's coming down the road.
Think of it like building a bridge. First, you have to know how much traffic it needs to handle (forecast demand). Then, you check the strength of the current bridge (measure capacity). After that, you see if the existing structure can handle the load (analyze the gap). Finally, you reinforce it or build a new one (implement the plan).
Step 1: Forecast Future Demand
It all starts by looking ahead. You need to predict what your customers will need from you, not by guessing, but by making smart, data-driven projections. A solid forecast is the bedrock of the entire process.
To build one, you’ll want to pull from a few key sources:
- Historical Data: Look at your own past performance. What were sales figures, website traffic, or support tickets like last year? Look for seasonal patterns and trends.
- Market Trends: Step outside your own four walls. Are there industry shifts, new technologies, or economic factors that could nudge demand up or down?
- Business Initiatives: Don't forget to look at your own roadmap. A new product launch, a major marketing campaign, or expansion into a new territory will all create new demands on your system.
By weaving these threads together, you get a much clearer picture of the future, letting you plan proactively instead of constantly fighting fires.
Step 2: Measure Current Capacity
Once you know what's coming, you need to get brutally honest about what you can handle right now. This means doing a full audit of your resources to set a clear baseline. You can't figure out what you need if you don't know what you've got.
This measurement needs to be thorough. For a software company, that means knowing the exact limits of your server CPU, memory, and storage. For a consulting firm, it's about calculating the total number of billable hours your current team can deliver.
A classic mistake is assuming you can run at 100% theoretical capacity. You can't. Always factor in the real world—employee vacations, system maintenance, and unexpected hiccups—to land on your true effective capacity.
Step 3: Analyze the Gap
This is where the rubber meets the road. You take your demand forecast from Step 1 and lay it right next to your current capacity from Step 2. The goal is simple: find the mismatch between what you will need and what you currently have.
The result will be one of two things: a shortage (demand outstrips your capacity) or a surplus (you have more capacity than you need). A shortage can lead to lost sales and frustrated customers. A surplus means you're bleeding money on idle resources. The key here is to identify exactly how big that gap is and when it's going to hit.
The diagram below shows how different planning horizons—long-term strategic, mid-term tactical, and short-term operational—all work together to bridge these gaps over time.
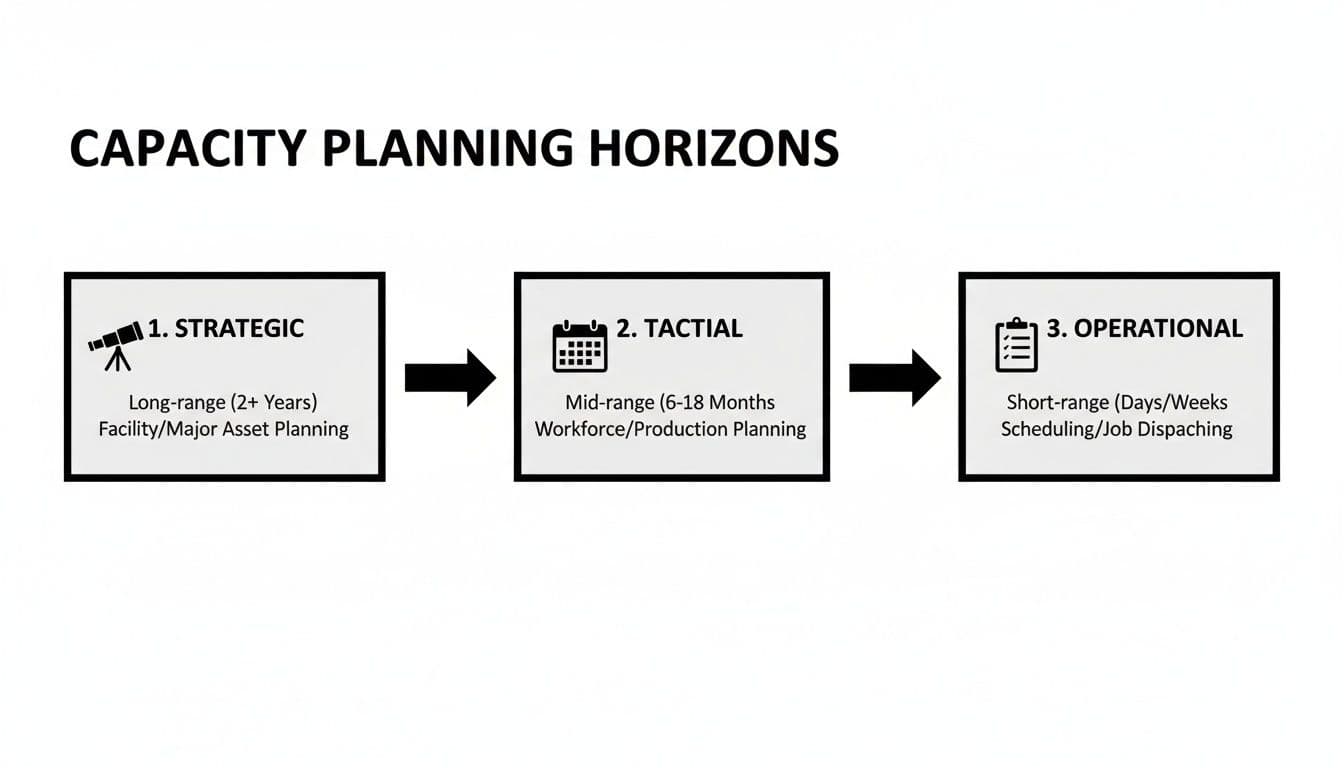
As you can see, the big-picture strategic decisions cascade down into tactical adjustments and finally into the daily operational tweaks that keep everything running smoothly.
Step 4: Implement the Plan
With a clear picture of the gap, the last step is to build a plan to close it and put that plan into motion. The right move depends entirely on the problem you've uncovered.
If you're facing a capacity shortage, you might:
- Acquire More Resources: This could be anything from hiring new people and buying new machines to spinning up more cloud servers.
- Get More Efficient: Before you spend money, see if you can squeeze more out of what you already have. Think process automation, better training, or optimizing your workflows.
If you're looking at a capacity surplus, you could:
- Reallocate Resources: Put those idle people or equipment to work in another part of the business where they can create value.
- Stimulate Demand: Run a marketing campaign or a sales promotion to put that excess capacity to profitable use.
This four-step cycle—Forecast, Measure, Analyze, Implement—isn't a one-and-done project. It's a continuous loop that keeps your organization nimble and ready for what's next.
Choosing the Right Capacity Planning Model
Once you have a framework in place, the real work begins: picking the right analytical tools for the job. Effective capacity planning hinges on strong models that can translate raw data into clear, strategic insights. Think of these models as different lenses for viewing the future; each one offers a unique perspective to help you make smarter decisions.
Let's walk through four powerful methods that pros use to cut through the noise of future demand and align their resources. Mastering these is the key to shifting from constantly putting out fires to proactively building a resilient strategy.
Forecasting Models
Forecasting is the bedrock of any serious capacity plan. It’s all about using historical data and market signals to make an educated guess about what's coming next. Without a solid forecast, you're flying blind, and aligning your resources becomes pure guesswork.
The most common approaches are fairly intuitive:
- Trend Analysis: This is about looking at past data to spot patterns you can project into the future. A retailer, for instance, would analyze the last five years of sales data to get a handle on what to expect for the upcoming holiday rush.
- Regression Analysis: This is a step up, helping you understand the relationship between different variables. A software company might use regression to see how a bump in marketing spend or a new feature release affects user sign-ups and, consequently, their server load.
Getting forecasting right is absolutely critical, but it's where many organizations stumble. A recent survey found that only 13% of companies feel their forecasting is 'extremely effective', and nearly two-thirds admit it's one of their biggest operational headaches. This just goes to show how tough it is to connect capacity with demand. You can dig into the full capacity planning statistics on Runn.io to see just how widespread these challenges are.
Queuing Theory
Ever stood in a grocery store line and wondered why there are eight checkout lanes but only five are open? You've just bumped into queuing theory. It's a mathematical way to analyze waiting lines, or "queues," to keep things moving without costly delays and frustrating bottlenecks.
Think of your customer support team as the checkout lanes and incoming support tickets as the shoppers. Queuing theory helps you find concrete answers to questions like:
- How many agents do we need on staff to answer 95% of calls within 60 seconds?
- What's the real impact on customer wait times if one of our agents calls in sick?
- If we're bracing for a 20% jump in ticket volume after a big product launch, how many more agents should we have ready?
By modeling the arrival rate of tasks (customers) and the service rate of your resources (agents), you can find that sweet spot—the optimal balance that keeps things flowing smoothly without having expensive resources sitting idle. It's an incredibly powerful tool for any service-based operation where managing wait times is everything.
Utilization Analysis
Utilization analysis is as straightforward as it is essential. It simply measures how much of your available capacity is actually being used. The formula is easy: (Actual Output / Maximum Possible Output) x 100.
For example, if a factory has the machinery to produce 1,000 widgets a day but is currently making 800, its utilization rate is 80%. In the tech world, if a server's CPU is humming along at 40% of its total processing power, its utilization is 40%.
Now, it might seem like the goal is to hit 100% utilization, but that’s usually a recipe for disaster. Both systems and people need some breathing room to handle unexpected surges. Running at or near full capacity leaves no margin for error and leads to employee burnout, system crashes, and the inability to jump on a sudden opportunity. The real art is finding the right balance—a utilization rate that's efficient but not dangerously close to the breaking point.
Simulation Models
What if you could test-drive your capacity plan against thousands of possible future scenarios before spending a single dollar? That's exactly what simulation models let you do. They are computer-based replicas of your real-world operations, allowing you to run "what-if" scenarios to see how your system holds up under pressure.
One of the most popular techniques here is the Monte Carlo simulation. Instead of plugging in a single, fixed number for a variable like customer demand, you give it a range of possible values. The simulation then runs hundreds or thousands of times, picking random values from that range for each run. What you get isn't one single answer, but a full probability distribution of potential outcomes. Anyone building predictive tools needs to understand these concepts, and you can see similar principles at work by exploring financial modeling best practices.
This approach is priceless for navigating uncertainty. A logistics company could use a simulation to see how different levels of port congestion or wild swings in fuel prices would affect its delivery times and bottom line. By stress-testing the plan this way, you can spot the weak points and build a much more resilient strategy from the start. As you select your model, always be thinking about improving forecast accuracy, because the quality of your entire plan depends on it.
Essential Tools And Metrics For Measuring Capacity

Effective capacity planning comes down to a simple, unshakeable truth: you can't manage what you don't measure. To move beyond guesswork and build a truly data-driven strategy, you need to get comfortable with the numbers. Key performance indicators (KPIs) are the dashboard for your business, giving you a real-time view of your operational health and flashing warning signs when things need to change.
Without solid data, your plans are just theories. By defining and consistently monitoring the right metrics, you gain the clarity needed to make confident decisions on everything from hiring new team members to investing in technology. This is where the abstract concept of planning becomes a concrete business advantage.
Core Metrics That Drive Capacity Decisions
While every industry has its own unique KPIs, a few fundamental metrics form the bedrock of almost any capacity plan. Getting these right is the first, most crucial step toward optimizing your resources.
-
Utilization Rate: This is the big one. It simply tells you what percentage of your available capacity is actually being used. The formula is (Actual Output / Maximum Possible Output) x 100%. For a server, this might be its CPU usage. For a consulting team, it's their billable hours. While high utilization seems great on the surface, pushing past 85-90% consistently is a red flag. It often means your systems or people are overworked, leaving no room for unexpected spikes in demand and increasing the risk of burnout or failure.
-
Throughput: Think of this as your productive output. It measures how much work gets done over a specific period. A factory might measure units produced per shift, while a software team could track features deployed per quarter. Watching your throughput helps you spot bottlenecks and understand how much you can really get done.
-
Response Time: This is the time it takes to get something done from the customer's perspective. For a call center, it’s the time until a caller speaks to a live agent. For an e-commerce site, it’s the page load time. When response times start to creep up, it's one of the earliest and clearest signals that demand is starting to outpace your capacity.
These metrics are essential for building a leaner, more effective business. To see how they fit into the bigger picture, take a look at our deep-dive on what is operational efficiency.
Consistently tracking utilization, throughput, and response time creates a powerful feedback loop. This data-driven approach lets you spot trends, predict future needs, and proactively adjust your capacity before small issues snowball into critical problems.
To give you a handy reference, here’s a quick summary of these essential metrics.
Key Capacity Planning Metrics at a Glance
| Metric | Formula / Definition | What It Measures |
|---|---|---|
| Utilization Rate | (Actual Output / Maximum Possible Output) x 100% | The percentage of available capacity currently in use. |
| Throughput | (Units Produced / Time Period) | The rate at which work is completed over time. |
| Response Time | (Time Request Fulfilled - Time Request Made) | The total time taken to fulfill a request from start to finish. |
| Efficiency | (Standard Labor Hours / Actual Labor Hours) x 100% | How well resources are used compared to a set standard. |
| Backlog | The total volume of work waiting to be processed. | The accumulation of unmet demand, indicating a capacity shortfall. |
These metrics provide the raw data you need, but you'll also need the right tools to collect, analyze, and act on it.
Essential Tools For Capacity Management
Gathering and making sense of all this data would be nearly impossible without the right technology. The tools you pick will depend on your company's size and the complexity of your operations, but they usually fall into one of three main buckets.
-
Spreadsheets (Excel, Google Sheets) For small businesses or for those just dipping their toes into formal planning, you can't beat a good spreadsheet. They are perfect for basic calculations, manually tracking a few key metrics, and building simple forecasting models without a big investment.
-
Specialized Capacity Management Software As your needs grow, dedicated software becomes a game-changer. These platforms automate data collection, offer advanced analytics, and run sophisticated simulations for "what-if" scenario planning. They often integrate with other business systems to give you a single, unified view of capacity across the entire organization.
-
Cloud Provider Dashboards If your business runs on public cloud infrastructure, the native tools are indispensable. Services like AWS Cost Explorer or Azure Advisor provide incredibly detailed dashboards on resource utilization, performance, and costs. This real-time visibility is absolutely critical for managing dynamic and scalable environments.
The market for these tools is exploding for a reason. Valued at $597.5 million in 2018, the global capacity management market is projected to skyrocket to nearly $5.48 billion by 2030. That growth, at an annual rate of about 20.3%, underscores just how critical optimized resource management has become in today's business world. You can read the full global capacity management market research for more details on this trend.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid in Capacity Planning
Even with the sharpest models and the clearest metrics, a capacity plan can go off the rails fast. There are a few classic mistakes that trip up even experienced teams, turning a forward-thinking strategy into a reactive fire drill. Knowing what these traps look like is the first step toward sidestepping them entirely.
One of the most common blunders is planning in departmental silos. Picture this: the sales team is forecasting a record-breaking quarter, but that memo never makes it to the IT or operations teams. When the orders flood in, the website crashes and the warehouse can't keep up. It's predictable chaos, all because the left hand didn't know what the right hand was planning.
Over-Reliance on Historical Data
Leaning too heavily on past data is another big one. Looking at historical trends is a great place to start, but it's like driving by only looking in the rearview mirror. It won't tell you about the sharp turn ahead—like a competitor's surprise product launch or a sudden shift in the market. A plan built solely on yesterday's numbers is fragile and will shatter as soon as something new happens.
Smart planners know this, so they mix the hard numbers with on-the-ground intelligence. They’re constantly talking to the sales team about upcoming promotions and gathering insights on what competitors are up to. This blend of quantitative and qualitative information creates a forecast that’s far more resilient and realistic.
A successful capacity plan is a living document, not a one-time report. It must be regularly reviewed and adjusted as new information becomes available, creating a feedback loop that keeps the business aligned with reality.
Misalignment with Business Objectives
Maybe the most dangerous mistake of all is creating a capacity plan that’s disconnected from the company’s real goals. For instance, a plan to slash IT server costs by 10% might look great on a spreadsheet. But if the company's number one goal is aggressive growth and market capture, that "cost-saving" move could end up starving the business of the very resources it needs to win.
To avoid this, every capacity decision has to support the big-picture strategy. The question should always be, "How does this resource plan help us achieve our primary objectives?"
Here are a few other common missteps to keep on your radar:
- Ignoring a Feedback Loop: If you're not constantly reviewing and tweaking the plan, it becomes obsolete almost immediately.
- Forgetting About Inefficiencies: Before you spend money on more resources, ask if you can get more out of what you already have. You'd be surprised how much capacity can be unlocked with smarter processes. You can explore some powerful business process improvement techniques to see what’s possible.
- Neglecting 'What-If' Scenarios: A plan that hasn't been tested against potential disruptions—like a supply chain crisis or a sudden economic downturn—is a plan that's waiting to fail.
By actively steering clear of these traps, you can build a capacity plan that doesn't just put out fires. You'll have a roadmap that truly drives sustainable growth.
Frequently Asked Questions About Capacity Planning
Even with a solid framework in place, a few common questions always seem to pop up when teams start putting a capacity plan into action. Let's tackle some of the most frequent ones.
Capacity Planning Versus Resource Planning
People often use these terms interchangeably, but they operate at completely different altitudes. It helps to think of it this way: capacity planning is the architect designing a skyscraper, figuring out the total number of floors and offices it can support. Resource planning is the construction foreman deciding which specific crew gets assigned to frame the 10th floor on Tuesday.
Capacity planning is strategic. It answers big-picture questions like, "Do we have enough server power to get us through the next two years of growth?" Resource planning is tactical. It’s all about allocation: "Which engineer is free to tackle this bug fix tomorrow morning?"
The core difference is scope and timeline. Capacity planning defines the total potential output your business can achieve, while resource planning allocates the specific inputs needed to complete current tasks and projects.
How Often to Review a Capacity Plan
There's no magic number here; the right cadence depends entirely on which type of plan you're looking at. The biggest mistake you can make is to create a plan, file it away, and forget about it. It needs to be a living document.
A good rule of thumb is to follow this rhythm:
- Strategic Plans (Long-Term): Revisit these annually or after any major business shift, like a new product launch or an acquisition.
- Tactical Plans (Medium-Term): These need a closer look, usually quarterly or semi-annually, to align with updated sales forecasts or project roadmaps.
- Operational Plans (Short-Term): This is the day-to-day stuff. Reviewing workloads and schedules weekly or even daily is pretty standard to keep things running smoothly.
Is Capacity Planning for Small Businesses
Definitely. The fundamental goal—matching what you have with what you need—is just as crucial for a five-person shop as it is for a global corporation. A small business might not need a complex software suite, but the underlying thinking is essential for growth.
For a startup, capacity planning might be as simple as a spreadsheet model that helps decide when to hire your first salesperson or whether you can afford that bigger office space. It’s the discipline that keeps you from getting overwhelmed by your own success or, just as bad, from spending cash on resources you don't actually need yet.
Ready to ace your consulting or finance interview? Soreno provides an AI-powered platform with over 500 cases and personalized feedback to help you land your dream job. Practice with an AI interviewer trained on MBB methodology and get detailed analytics on your performance. Start your 7-day free trial at https://soreno.ai.